News
View the latest inspiring and positive news and information about what's going on in the PM and IT world.

How important is the technological competence of the Scrum Master? At times it may seem like the Scrum Master is a simple motivator with management skills rather than IT, or is it the link between the product owner and the team?
By carefully reading the guide to Scrum by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland we find no reference to “Technological” competencies of the Scrum Master. But it is absolutely possible that the Scrum Master is also part of the Development Team.Do customers easily accept to pay a Scrum team for a specific period without however being certain of the final result?
If you are used to procurement through “Fixed Scope” contracts, it can be difficult to change even if the goal is to seize an opportunity. Remember, Agile is a mindset. Therefore it is necessary for everyone (Customer / Supplier) to evolve; from a “closed” approach, with low external sharing, it is necessary to gradually move to an “open” approach, based on a cycle of learn-share-collaborate-improve, to encourage the exchange and transfer of knowledge in unconventional ways.What responsibility does the Scrum Master usually have in the context of cost and time control of a project?
The Scrum Master has many responsibilities (that you can discover here), but among these, there are no items that specifically concern the management of Time & Cost project constraints. It is a shared responsibility of the entire Scrum Team. Remember that Time & Costs are fixed and that the Scrum Team must be “Good” in setting the Sprint Goal. Here you can discover the responsibilities of the other Scrum Team members; the Scrum Developer and the Scrum Product Owner.If after multiple sprints the sprint goal is not reached, is this a failure for the Scrum Master? And what approach should the Scrum Master take in this circumstance?
The situation described is not a failure for the Scrum Master but certainly is a reason for reflection for the entire Scrum Team; issues to reflect on could be:- What did we not understand about the project/product?
- Is there a technical knowledge gap to fill?
- Internal/external changes to the client that make the sprint goal systematically obsolete?
But if the objectives are not reached during the sprints, does that mean that the time of the project is prolonged? If so, how does that work with the costs?
When the approach is Predictive in the early stages of the project, the focus is on detailing the planning by basing the estimates on the Scope defined in the formal documents (plan-driven approach). During the life cycle of the project, the project plan will be the work management guide and the reference for calculating progress. Changes are managed through a formal system and the value is generated at the end of the project, upon delivery of the final product. When, on the other hand, the requirements are unstable it is advised to focus on making decisions that give priority, and therefore time precedence, to activities with greater added value and actions for greater risk reduction (value-driven approach). It is advised to set budgets and create a plan in advance and to make the project scope negotiable. This rather than trying to fix the characteristics of the product, which will consequently determine the times and costs of implementation (plan-driven approach). When the approach is adaptive, therefore, the planning is carried out iteratively before each Sprint/Iteration, you are able to respond quickly and effectively to change. This results in a reduction in costs and, ultimately, an increase in profitability and Return on Investment (ROI). In more general terms, we move from an “inside-out” model, where you make and sell your product on the market, to an “outside-in” model, where you iteratively build the product/service together with your customer. Here the focus is on the Minimal Viable Product (MVP).Does the Scrum Product Owner also participate in the Sprint Retrospective phase? If so, what role does he/she play in the development team?
The Agile Business Consortium “strongly recommends” the presence of the Scrum Product Owner during the Sprint Retrospective meeting; like all members of the Scrum Team, he/she introspects and actively participates with the goal of continuous improvement.What does the Scrum Product Owner have to say during the daily? Isn’t that an obstacle to the Scrum Master in facilitating the ease of the team?
The Scrum Product Owner may be a member of the Development Team. This is a perfectly viable situation and in such circumstances, the Product Owner can obviously participate and participate fully in the Daily Scrums. If the Product Owner is not part of the Development Team, there are different schools of thought. Eg. Agile Alliance suggests keeping the Product Owner out of the Daily Meeting, Agile Business Consortium instead recommends the participation of the Product Owner and suggests the Development Team invite the Product Owner (it’s a good idea to share the choices and the commitment).
 Antonietta-Fiorentino
Antonietta-Fiorentino
Antonietta Fiorentino is an entrepreneur and Transformation Leader. Bi-modal PMO in digital transformation and for the innovation of large and medium-sized enterprises.
For QRP she is a trainer and agile business consultant.

Why such a change?
The latest PMI market research shows that CAPM certification holders believe that PDUs represent a more valuable investment of their time and effort, as they allow them to keep abreast of new developments and trends in project management. This new process is easier and less costly for CAPM certification holders as there are many ways to earn PDUs. If CAPM certifiers obtain other PMI certifications, the PDUs they earn with the other certifications can be applied to the CAPM PDU requirements. They will simply have to pay the recertification fee. Thus, if the professional becomes certified (PMP), they can count 15 of the 60 PDUs they earn for the PMP towards their CAPM PDU requirements.Limited time renewal offer
To facilitate the transition from PDU acquisition to maintaining CAPM certification, the following limited-time renewal offer is available: Active CAPM certification holders who renew at the member and non-member price of USD 60 by 31 March 2021 will have an additional three years to their certification cycle. This will give certification holders more time to adjust to obtain the 15 PDUs needed to maintain certification. In addition, regardless of when individuals pass the CAPM certification exam, they can take advantage of this offer. However, those who do not renew by March 31 2021, will need to earn the newly required 15 PDUs before their certification expires, log on to the CLS and pay the renewal fee ($60 member / $150 non-member) to maintain their certification. Holders of expired CAPM certification who take advantage of the member and non-member renewal price offer of $60 USD by March 31 2021 will have their CAPM certification reinstated for three years. For more information, contact our team at switzerland@qrpinternational.com Source: https://www.pmi.org/
MSP 4 vs MSP 5
The essence of what a program remains the same as it was with the 4th edition: it is temporary, it is focused on results and benefits, and it is concerned with leading several projects and other work. The basic concepts (principles, themes, and processes) also still form the overall structure of the guide. However, these have been revised with the following principles in mind:- Ensure that MSP remains adaptable and flexible and can be used in a wide range of organizations and environments. There are many different drivers of change, and the MSP approach to program management must ensure that the organization's investment in change is managed wisely.
- Provide guidance for a wide range of investments that benefit from program management, recognizing that the word "program" has many different meanings for organizations and that terms other than "programs" may be used by these organizations.
- Emphasize the incremental nature of a program and show how MSP allows cyclical progression to the desired future state. Organizations are complex, the external context is emergent, and the delivery of benefits and value creation generally cannot be achieved through a series of linear steps.
- Enable program teams to recognize the many ways in which outputs and changes can be delivered, including iterative (Agile), traditional, and hybrid approaches.
Key Elements of MSP 5
The MSP 5th edition emphasizes greater flexibility, adaptability, and responsiveness by taking an incremental approach to the program lifecycle and enabling organizational agility. The MSP 5th edition consists of a set of principles, themes, and processes that provide a clear roadmap for the program life cycle and ensure successful organizational results. The MSP guide offers 3 lenses:- 7 universal principles
- 7 themes facilitating governance and essential controls
- 7 processes representing the incremental life cycle which, if flexible and adaptable, allows an orderly cyclical progression with clear decision criteria.
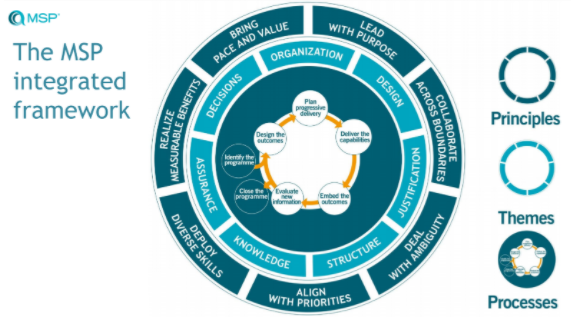 Source: webinar “OVERVIEW MSP 5th EDITION” - Axelos 2020
The overview of the revised key elements is as follows:
Source: webinar “OVERVIEW MSP 5th EDITION” - Axelos 2020
The overview of the revised key elements is as follows:
. Vision
An updated approach to the structure of a vision statement.. Benefits
A reinforced vision of a key principle of SHP throughout the guide.. Risks
A broader discussion of risks and risk mitigation across the program.. Organizational Structure and Roles
Well-established roles within the MSP have been reviewed and updated, and new roles are being introduced and discussed.. Business Case
One of the main challenges is to obtain funding for a program. In the updated basic guide, this topic is discussed and provides a new approach to its development.. Blueprint
A key element of MSP has evolved into the target operating model, and the MSP 5th edition explains its use and benefits in more detail.. Stakeholder Engagement and Communications Planning
Key elements of the new working methods, responding to the main challenges of today's program management.Agile Program Management Integration
The MSP 5th edition offers the multimodal delivery mode, which allows multiple ways of working, depending on what suits you best during delivery. The same program or project can combine different approaches to work, its components, with projects using iterative (agile), traditional or hybrid life cycles, or continuous improvement activities. Leaders need to decide when to invest in addressing change drivers, for example:- adopt disruptions and emerging technologies and trends,
- build new physical infrastructure,
- respond to societal expectations and policy changes,
- establish more effective working partnerships across supply chains,
- using scarce resources as efficiently as possible.
Main Differences between Exams
The MSP 5th edition certification scheme includes only two levels: MSP Foundation and MSP Practitioner. In addition to a completely redesigned program, there are several differences between the MSP 4th and 5th edition exams that will bring new benefits to candidates :- The MSP Foundation exam has been streamlined so that candidates can now focus on learning MSP content, rather than learning to answer complex questions.
- The MSP Practitioner exam has also been simplified to give the candidate more time on the exam to focus on the questions and reduce the reading load.
- Both exams have seen a reduction in the number of questions for each level: the MSP Foundation exam has been reduced from 75 to 60 questions, and the MSP Practitioner exam has been reduced from 80 partial questions to 70 questions. Despite the reduction in complexity and number of questions, the time allocated to write the exams remains at 60 minutes and 150 minutes respectively for MSP Foundation and MSP Practitioner. This is to ensure that candidates have sufficient time to be able to answer each question to the best of their ability.
- Both exams have been refocused based on the cognitive ability (Bloom level) required. The MSP Foundation exam covers all key concepts at the level of knowledge and understanding (Bloom's 1 and 2). There are no new concepts introduced at the MSP Practitioner level; the exam simply assesses the same concepts at a higher cognitive level (Bloom's 3 and 4), where the candidate is asked to apply and analyze the concepts in context.
Benefits of the MSP 5th Edition Method
- It aligns projects and programs with organizational strategy.
- It provides a disciplined approach to profit management that facilitates business changes.
- It ensures an appropriate division of responsibilities and obligations.
- It facilitates organizational agility.
- It helps to understand the risks associated with a program.
- It is a proven best practice in the successful implementation of organizational change through the application of program management.
Would you like to follow an MSP training course?
Our training is once again available in face-to-face and distance learning. QRP is ISO 9001:2015 certified. Contact our team at +41 (0)43 588 10 36 or switzerland@qrpinternational.com to learn more about our virtual classroom, face-to-face, or intra-company offers!
Why QRP?
QRP is a PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP). To maintain this designation, we must continuously meet rigorous standards for quality and effectiveness. As ATP we completed the PMI Train the Trainer – PMP Exam Prep® program and we use PMI-developed training course content. Training with an Authorized Partner will ensure you are trained:- By an organization you can trust,
- With high-quality PMI-developed course content,
- By PMI-approved instructors.
- quality training,
- licensed content for Project Management Professional (PMP)®,
- online learning assets like quizzes, knowledge checks and videos,
- trainers with a badge that shows they are PMI-approved instructors,
- assistance from the trainer for the exam subscription (if applicable).
Still not convinced?
Our PMP courses include the PMBoK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) in its last edition (6th edition, for now, 7th edition as soon as it will be launched) which represents good practice for most projects most of the time. Any PDU claim made against a course delivered by QRP will automatically be accepted by PMI without audit. You can choose between different course formats: we offer classroom, virtual and corporate training. QRP has 20 years’ experience delivering Project Management training across the world. Our trainers are carefully selected from our specialized network. Most trainers are accredited on multiple Best Practices. QRP offers classroom, virtual and corporate training. Visit our PMP exam preparation course page to know all details! For any questions, feel free to contact us directly.

When is the new review effective?
The new PMP review is effective from 2 January 2021. As a reminder, it has been possible to take the PMP exam online since April 2020. It will take 3/4 days to find an online exam session. You can therefore find a place in an examination center quickly. The exam is accessible 7 days a week, 24 hours a day.Why such a change?
The PMI is following a certain process to evolve this standard of examination. The new examination is reflected in a document called the "PMP examination content outline". This is the preferred document for preparing for the examination (available in pdf). This change is made to maintain PMI's accreditation. PMI follows two standards, ISO 17024 and ISO 9001, and must comply with certain requirements. Consequently, the PMI has the obligation to conduct a field survey every 4/5 years in order to meet with professionals in the sector and understand what their needs are, what knowledge is required, what skills are needed, what are the daily tasks for a project manager. This survey allows the PMI to carry out a worldwide market study from which the PMI updates its certification so that the examination best reflects the needs on the ground.What's changing in the PMP Exam?
Currently, these outlines of the examination content are valid until 31/12/2020 and reflect 5 areas and 42 tasks.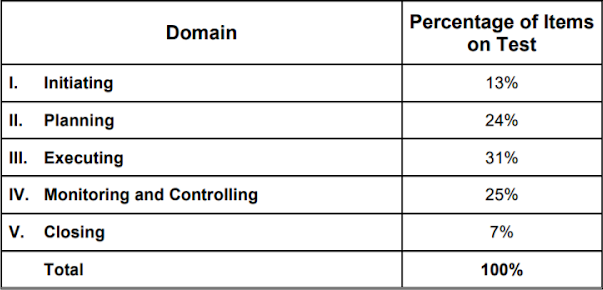 The survey identified market developments and trends.
PMBOK 7th edition and the new review reflect the reality on the ground and take into account the fact that today's project management professionals work in a variety of project environments and use different project approaches.
The new PMP certification will reflect this and integrate approaches across the spectrum of value delivery. Approximately half of the exam represents predictive project management and the other half represents agile or hybrid approaches.
These approaches cut across the three areas listed above and are not isolated to any particular area or task.
The survey identified market developments and trends.
PMBOK 7th edition and the new review reflect the reality on the ground and take into account the fact that today's project management professionals work in a variety of project environments and use different project approaches.
The new PMP certification will reflect this and integrate approaches across the spectrum of value delivery. Approximately half of the exam represents predictive project management and the other half represents agile or hybrid approaches.
These approaches cut across the three areas listed above and are not isolated to any particular area or task.
The 3 new areas
The three new domains are now aligned with the PMI Talent Triangle, presented in the PMBOK 6th edition.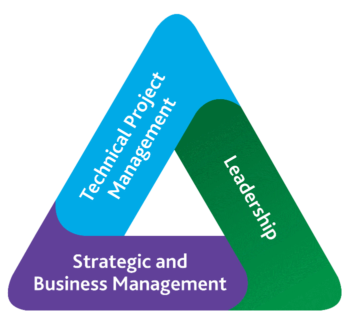 We find:
We find:
 . The people (human) domain
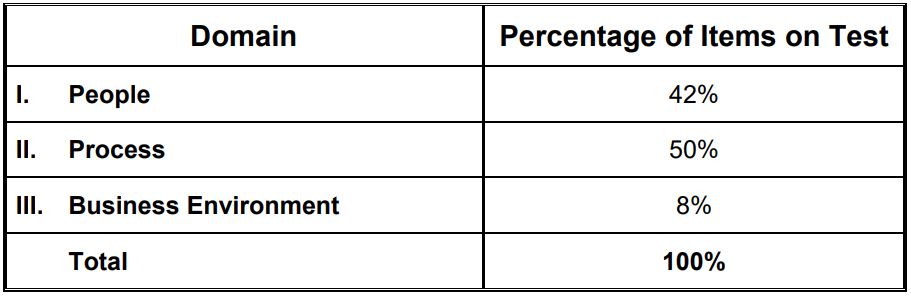
14 tasks - 42% of the questions under consideration.
It covers leadership, conflict management, virtual team management, emotional intelligence, soft skills.
. The process domain (processes)
17 tasks - 50% of the questions under review.
It covers all processes with the 10 PMBOK knowledge areas, the appropriate project management approach, governance, and value.
. The people (human) domain
14 tasks - 42% of the questions under consideration.
It covers leadership, conflict management, virtual team management, emotional intelligence, soft skills.
. The process domain (processes)
17 tasks - 50% of the questions under review.
It covers all processes with the 10 PMBOK knowledge areas, the appropriate project management approach, governance, and value.
. The business environment domain (the business environment) 4 tasks - 8% of the questions under review. It covers compliance, profit realization, organizational change, the external environment, and links the organization's strategy to the project.
Here is an example:
Format of the new PMP examination
The new examination includes:- 180 questions (the previous exam was 200) but the same number of questions will be scored
- 230 minutes to complete the exam
- Two 10-minute breaks
- The questions will be a combination of multiple-choice, multiple answer, matching, hotspot, and limited fill.
Prerequisites for the new PMP exam
Before applying for the examination, the participant must ensure that the following pre-requisites are met: If you have a four-year degree or higher :- Have more than 36 months of experience in project management,
- 35 hours of training in project management*.
- A high school diploma
- Have more than 60 months of experience in project management
- 35 hours of training in project management*.
How to prepare for the exam?
Reading
The PMI provides a list of suggested documents and books to help you prepare. QRP simply advises you to read the PMBOK 6th edition (included in the training cost), while waiting for the release of the PMBOK 7th edition, scheduled for 2021, and the Agile Practice Guide.Training Kit (included in the training cost)
The PMI now offers a complete training kit based on the new examination, which can be described as an official kit, called the "PMI CHOICE". It includes an electronic version of a PMP certification preparation course material that can be downloaded in PDF format or viewed and annotated online from various media (PC, iPad/iOS tablets, Android) as well as numerous short videos of 3 to 6 minutes to facilitate learning. Some additional tools are also provided such as the TO-DO LIST, a must for any project manager, various quizzes to self-assess yourself, and a set of 200 questions from the new 2021 exam. Please note: the CAPM® certification exam does not change. The PMI recommends using instructors with an instructor badge. Indeed, to obtain the quality of instructor accredited by the PMI, it is necessary :- To have a valid PMP certification,
- To have significant experience in Agility,
- To have followed a PMI "train the trainer" training course,
- To have passed the instructor's exam (to obtain their badge),
- To be attached to an ATP (Authorized Training Partner) as QRP International.
What is PMI ATP?
 An Authorized Training Provider (ATP) is a training organization accredited by the PMI to provide training in preparation for PMP certification. Attending training with an ATP guarantees you formal training, with official course materials (provided by the PMI) and an accredited and certified instructor with a valid badge.
QRP International is an ATP training organization, check out our PMP training calendar!
An Authorized Training Provider (ATP) is a training organization accredited by the PMI to provide training in preparation for PMP certification. Attending training with an ATP guarantees you formal training, with official course materials (provided by the PMI) and an accredited and certified instructor with a valid badge.
QRP International is an ATP training organization, check out our PMP training calendar!
Organizational change management
When we talk about Change Management in the IT field, we tend to emphasize the technological aspect, for example, the development of functionality or changes to infrastructure. The more significant the change, the more it has an impact on the daily life of resources. Therefore the “soft” aspect of change must also be managed. Organizational Change Management is linked precisely to changes in the human environment. Organizations need to become aware of these aspects as well: in the past, IT projects have been predominantly seen as technology-only projects. According to the definition of ITIL 4, the practice of Organizational Change Management“ensures that changes are implemented successfully and effectively within an organisation and that long-term benefits are achieved by managing the human aspect of changes.”ITIL 4 identifies the objectives and benefits of Organizational Change Management and what resources to involve in this practice.
Objectives:
- Convince all the resources involved in the change about the positive impact.
- Reduce or remove resistance to change.
- Ensure that change is successfully implemented and supported.
- Facilitate the transition of resources, teams, and the organization to the desired future situation.
Benefits:
- Improvements are implemented smoothly and with lasting benefits.
- Resources understand the goal of the changes and their impact on work.
- Resources believe in the importance and benefits of changes.







